What Can I Learn About the Legislative House of Representatives
- Introduction
- What is the Legislative Branch?
- What does the House of Representatives practice?
- Boosted Resources
- Ways to Get Involved/What You Can Do
- Suggestions for Your Next Chat
Introduction
 The United States spent eight long years of drastic fighting for independence from 1775 to 1783. By 1789, the Founding Fathers had ready about constructing a authorities "built on the cardinal conviction of revolutionary-era republicanism: that no cardinal authority empowered to coerce or discipline the citizenry was permissible , since it only duplicated the monarchical and aloof principles that the American Revolution had been fought to escape. The United states of america is now the oldest enduring republic in world history, with a fix of political institutions and traditions that take stood the exam of time."
The United States spent eight long years of drastic fighting for independence from 1775 to 1783. By 1789, the Founding Fathers had ready about constructing a authorities "built on the cardinal conviction of revolutionary-era republicanism: that no cardinal authority empowered to coerce or discipline the citizenry was permissible , since it only duplicated the monarchical and aloof principles that the American Revolution had been fought to escape. The United states of america is now the oldest enduring republic in world history, with a fix of political institutions and traditions that take stood the exam of time."
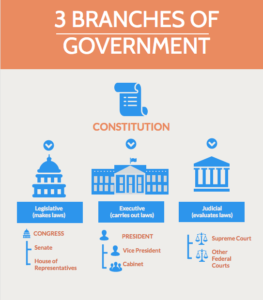
According to House.gov , "To ensure a separation of powers, the U.S. Federal Government is made up of three branches: legislative, executive and judicial. To ensure the authorities is effective and citizens' rights are protected, each branch has its own powers and responsibilities, including working with the other branches." This is often referred to as " checks and balances ," and prevents any one part of regime from wielding too much political ability.
Why it Matters
 America benefits from a judicial branch positioned to halt executive branch overreach. The President of the United States cannot stay in power indefinitely and is unable to strength the U.S. Congress to pass laws. From the very get-go, and still to today, the American people accept access to and influence over their elected representatives.
America benefits from a judicial branch positioned to halt executive branch overreach. The President of the United States cannot stay in power indefinitely and is unable to strength the U.S. Congress to pass laws. From the very get-go, and still to today, the American people accept access to and influence over their elected representatives.
The House of Representatives most directly reflects the desires of the American public due to the ratio of American citizens to U.S. Representatives and the constant election cycle every 2 years. Much of the deadlock of the U.Southward. government that nosotros witness today reflects a divided American people.
This brief focuses on the Legislative branch of the U.S. government, in particular the Firm of Representatives, including the nuts and bolts of how its inner workings, and how everyday citizens tin can influence the legislative process. For a brief on the U.S. Senate, click hither .
Salve Save
What is the Legislative Branch?
The legislative branch is made upwards of the House of Representatives and the Senate , known collectively as the Congress. Amid other powers, the legislative branch "makes all laws, declares war, regulates interstate and strange commerce and controls taxing and spending policies."
CrashCourse U.S. Authorities and Politics, produced in collaboration with PBS, explains the Bicameral Congress (9 min):
Of all federal government institutions, the Business firm of Representatives is designed to be closest to American voters, most closely reflecting the individual cares and concerns of American taxpayers. In fact, the Business firm is the only establishment that has been directly elected by American voters since its formation in 1789.

"'If proportional representation takes place, the small States contend that their liberties volition exist in danger. If an equality of votes is to be put in its place, the large States say their money will be in danger,'" explained Benjamin Franklin . What somewhen "emerged from weeks of stalemate was called the 'Great Compromise' and created a bicameral legislature with a Firm, where membership was determined by land population, and a Senate, where each land had two seats regardless of population."
Size and Construction of the House
In that location are 435 representatives in the Business firm , and have been since the number was stock-still past law in 1911. Each House representative is elected to a two-year term serving the people of a specific congressional commune in a state. "Each country receives representation in the House in proportion to the size of its population simply is entitled to at least one representative." This means that states with large populations have more representatives than pocket-size states have. Representation based on population was "one of the virtually important components of the Federal Constitutional Convention of 1787," every bit one of the founders' greatest concerns was designing a organization of regime that would improve represent the public than did the British model from which they had won independence.
In improver to the 435 representatives from the states, in that location is a Resident Commissioner from Puerto Rico and Delegates from Washington D.C., American Samoa, Guam, The Republic of the Northern Mariana Islands, and the Virgin Islands. The Resident Commissioner and Delegates are able to serve and vote on committees, but do not have the same total voting rights as the 435 land representatives.
The Part of the Census
Specifically, seats in the Firm " are apportioned based on state population co-ordinate to the constitutionally mandated Census." The Census, which occurs every ten years and is overseen by the Bureau of the Census, office of the U.S. Department of Commerce. Tying representation to Census data allows the number of each country's representatives to increment or decrease along with fluctuations in state population. The Census data is then used to determine congressional districts, areas in the state from which representatives are elected to the Firm. This procedure is called redistricting. For more on redistricting and the Census, see The Policy Circumvolve'southward Decennial Census Brief.
 Elections
Elections
Members of the House of Representatives " must represent election every two years , after which it convenes for a new session and essentially reconstitutes itself – electing a Speaker, swearing-in the Members-elect, and approving a slate of officers to administer the institution." Biennial elections are held in November, and the Congress commences in the following January. To be elected, a representative must exist at least 25 years old, a United States citizen for at least seven years, and a resident of the country he or she represents. U.South. House candidates are not required to live in the congressional district they represent.
The Life of a Representative
Co-ordinate to Congressional Direction Foundation's Life in Congress study , when representatives are in Washington, D.C., they study spending their fourth dimension as follows:
- 35% on "Legislative/Policy Work"
- 17% on "Constituent Services Piece of work"
- 17% on "Political/Campaign Piece of work"
- nine% on "Press/Media Relations"
- 9% on "Family unit/Friends"
- 7% on "Administrative/Managerial Piece of work"
- vi% on "Personal Fourth dimension"
When in their home district, they reported spending time as follows:
- 32% on "Constituent Services Work"
- eighteen% on "Political/Campaign Work"
- 14% on "Press/Media Relations"
- 12% on "Legislative/Policy Work"
- 9% with "Family/Friends"
- 8% on "Personal Time"
- 7% on "Authoritative/Managerial Work"
Compensation
Article I, Section 6 of the Constitution requires Congress to determine its own pay. Congress'south " current automatic adjustment formula , which is based on changes in private sector wages," was established by the Ethics Reform Act of 1989. The last pay aligning was in January 2009. Since, most representatives earn $174,000 annually, while the majority and minority leaders make $193,400. The Speaker earns the largest salary at $223,500. Additionally, representatives "are discipline to some specific laws and regulations regarding the credence of gifts ," particularly gifts from registered lobbyists or from private entities that retain or utilise a lobbyist.
What does the House of Representatives exercise?
Responsibilities of the Business firm
Per the Constitution , the Firm and Senate together make and pass federal laws, introduce bills and resolutions, offer amendments, and serve on committees that enable members to develop specialized knowledge on the matters under that committee's jurisdiction. Though both make upwards Congress, in that location are a few distinctions between the two. In particular, the Constitution "provides that only the Firm of Representatives may originate acquirement bills, " and by tradition information technology as well originates cribbing bills.
Additionally, while the Constitution does not specifically mention investigations and oversight , "the authority to conduct investigations is implied since Congress possesses 'all legislative powers'." The House initiates impeachment proceedings and passes manufactures of impeachment (the Senate sits every bit a court to try the impeachment).
Finally, during a presidential election, the House of Representatives steps in if no candidate receives a majority of the total balloter votes. Each state delegation has one vote to choose the President from among the top iii candidates with the largest number of electoral votes.
Leadership in the House
After each ballot, the political party that wins the most representatives is designated the " Majority ." The other political party is the " Minority. " The majority party holds key leadership positions, such as Speaker of the House. The aforementioned party tin accept the majority in both the House of Representatives and the Senate, or the chambers can be split. Third parties rarely take enough members to elect their ain leadership, so independents generally bring together i of the larger party organizations to receive commission assignments.
The House is run past bulk dominion. When a majority of members vote to practice something in the House, it gets washed. Majority rule makes passing legislation relatively efficient, and that means that the party in the minority has less ability to set the agenda or laissez passer its proposals. This contrasts with the Senate, where a single senator – in the majority or the minority – can generally strength a vote or stop a bill in its tracks.
Business firm Leadership includes the Speaker of the House, Bulk and Minority Leaders, and Majority and Minority Whips.
The Speaker of the House is the presiding officer of the House, and is elected by the members of the Business firm. The Speaker administers the Oath of Function to House members, chairs sure committees or nominates committee chairs (namely the chairs of the House Administration Committee and the Rules Commission ), and appoints members of diverse committees and House staff. After the Vice President, the Speaker is second in line to succeed the Vice President.
Bulk and Minority Leaders correspond their corresponding parties on the House floor. Each is elected by his or her respective party. The majority leader is second to the Speaker and schedules legislative business, planning legislative agendas rather than serving on committees. The minority leader serves as the minority party'southward spokesperson, essentially the minority party'due south counterpart to the Speaker. He or she also chairs the minority party's committee assignment console.
Majority and Minority Whips serve as middlemen to betwixt their party leaders and members. They "maintain communication between the leadership of the political party and its members, marshal support for party positions on the floor, count votes on key legislation, and persuade wavering Members to vote for the party position."
The Speaker of the Firm is elected by the entire Firm of Representatives, while the Republican Conference and Democratic Caucus elect the other leadership positions. The Republican Briefing is the formal organization of Republican Members in the House, and the Democratic Caucus is that of the Autonomous Members.
Run across electric current House Leadership positions here.
The Function of Committees
Committees " are permanent panels governed by Business firm bedroom rules, with responsibleness to consider bills and issues and to take full general oversight relating to their areas of jurisdiction." Committees take unlike legislative jurisdictions, but each considers, shapes, and passes laws related to its jurisdiction, and monitors agencies, programs, and activities within their jurisdiction. Each committee has a chair that leads the total commission, and a ranking fellow member who leads the minority members of the committee. Committee assignment direct affects a representative's work in Congress. Later a Congressional election, political parties assign newly elected representatives to continuing committees
Crash Course U.Southward. Government & Politics explains what Congressional committees practise (eight min):
Some of the well-nigh well-known committees include:
- The House Committee on Ways and Means , which oversees all taxation, tariffs, and other revenue-raising measures.
- The Business firm Committee on Appropriations , which has jurisdiction over setting specific government expenditures.
- The House Committee on Strange Diplomacy , which has jurisdiction over foreign assistance and oversees national security developments affecting strange policy.
- The House Committee on the Judiciary, which oversees the judiciary and civil and criminal proceedings.
Most committees are regular continuing committees, which keep from one Congress to the side by side. There are besides select committees, special committees formed for a short period of time for a specific purpose such as an investigation, and in that location are several articulation committees with the Senate. Run into a total list of all House Committees here .
Legislation in the House
Legislation begins with an thought . Information technology may come up from a Congressman, a staffer, a elective, or a thought leader or expert on a given subject. Yous may call up the School House Stone video , which walks through the legislative process in an attainable way and is great to share with your kids (3 min):
Drafting Legislation
Working with House parliamentarians — lawyers and clerks who provide nonpartisan guidance on rules and procedures — and other Congressional staff on Capitol Hill, the Congressional representative's staff drafts the nib. The parliamentarians have specific expertise; they piece of work closely with staff in a non-partisan manner to draft the specific language of the beak. Staff works to build sponsors and cosponsors before the bill is introduced.
Introducing a Neb
Any Member, Delegate, or Resident Commissioner can introduce a bill when the house is in session by " placing it in the 'hopper, '" a box on the House Clerk's desk in the Capitol building. The Member who introduces the neb is known every bit the master sponsor. The bill is so formally assigned a number by the Clerk. A bill originating in the Firm will offset with "H.R." (for the House of Representatives, as opposed to "Southward." for the Senate). The Speaker'south function and then assigns that beak to its commission(s) of jurisdiction, which then assigns the bill to a subcommittee(s).
Committee Process
The Subcommittee seeks input from relevant departments and agencies and holds public hearings. Subsequently hearings, at that place is a markup on the legislation , in which "views of both sides are studied in detail and at the determination of deliberation a vote is taken to decide" whether or not the subcommittee recommends the bill to the full committee. In the full committee, the subcommittee reports on the bill; this coming together provides an opportunity for Members to amend the legislation. At that place is as well the possibility that the committee tables the bill or fails to accept activity , which prevents the bill from reaching the full Business firm. You lot can sentinel Firm Committee hearing videos here .
To get to the total Firm, the committee staff writes a report describing the purpose of the bill, why the pecker is recommended, and an analysis of each function of the bill and how the nib may affect existing law. A full commission marker-up and the decision of what legislation makes information technology to the House floor is tightly controlled past the Committee Chairman'southward office and leadership. When the legislation is reported favorably out of the total committee it awaits a decision by leadership to schedule time for it to be debated on the House flooring. This decision is a negotiation based on priorities of the committee and of leadership.
After a committee has reported a bill, the bill is placed on the calendar . This means the bill is eligible for flooring consideration, merely not that it will necessarily make it to the floor. In the Business firm, information technology is up to the majority party leadership to decide which bills the House will consider on the floor, and in what social club.
Committee on Rules
One time leadership has decided that a specific piece of legislation will receive floortime, the House Majority Leader alerts the committee of jurisdiction that the neb will exist considered on the House Floor, and this kicks off the Rules Committee process.
The Committee on Rules , or Rules Committee, is one of the oldest continuing committees in the House. The Committee is commonly known as "The Speaker'southward Committee" – prior to 1910, the Speaker chaired the Rules Commission, and today it is the mechanism by which the Speaker maintains control of the House Flooring. The Rules Commission is sometimes also referred to every bit " the traffic cop of the House ," equally it determines how much time will be immune for contend on each piece of legislation considered on the Business firm floor, and if any (and which) amendments volition be allowed to exist considered during the argue.
Well-nigh bills are considered nether a procedure known as suspension of the rules , "which limits argue to 40 minutes and does not allow amendments to be offered by members on the floor." Otherwise, the bill is considered under terms tailored for the detail bill. In this case, the House adopts a resolution called a special rule from the Rules Commission. After the Rules Committee reports the rule for considering the bill and the House votes to adopt the rule, the Business firm tin can then continue to the floor debate.
Flooring Debate
Once the rule has been adopted, the House normally considers the bill "in a procedural setting chosen the Committee of the Whole , which is substantially "the House assembled in a different course; it is a committee of the House equanimous of every Representative that meets in the House chamber." This procedure "allows members an efficient way to consider and vote on amendments."
After the floor debate on amendments and the underlying legislation, the Committee of the Whole reports to the full House, which then votes on the bill. The bill passes the House past a uncomplicated majority , 218 votes of the 435 full. Information technology then goes to the Senate and waits to be scheduled for flooring time.
See The Policy Circle'due south Senate Cursory to see how the procedure continues.
Boosted Resource
Glossary of terms
Different types of legislation
Alternative legislative procedures in the House
Means to Get Involved/What You Tin can Do
Measure & Identify : Who are the influencers in your state, canton, or community? Learn nigh their priorities and consider how to contact them
- Practice you lot know who your Congressional Representative is ? What near your country elected officials ?
- Runway your representatives' votes with GovTrack .
Reach out: You are a catalyst. Finding a common cause is a great opportunity to develop relationships with people who may be outside of your immediate network. All it takes is a small team of two or three people to set a path for existent comeback. The Policy Circle is your platform to convene with experts you want to hear from.
- Notice allies in your community or in nearby towns and elsewhere in the state.
- Foster collaborative relationships with colleagues, neighbors, friends, and local organizations to mobilize an effort to bring attention to your issue to your local Congressional office. Also reach out to community leaders to educate them and request their engagement on the issue.
Plan: Set some milestones based on your state'southward legislative calendar .
- Y'all can find the legislative calendar for the House of Representatives here .
- Don't hesitate to contact The Policy Circle team, communications@thepolicycircle.org , for connections to the broader network, advice, insights on how to build rapport with policy makers and establish yourself every bit a civic leader.
Execute: Give information technology your best shot. You can:
- Enquiry: Make sure y'all know the facts most the outcome you lot are raising. Government agencies, think tanks, and media outlets can all be skilful resource. Recollect to research all sides of the issue to make sure you lot understand diverse angles. You can too talk with people who are affected by the issue with which you are concerned; anecdotal information combined with measured data can be powerful.
- Write: Although we may be more inclined to email in the digital age, writing an old-fashioned letter to your local elected representatives or to members of Congress is yet one of the most effective ways to influence lawmakers.
-
-
- See these tips for pace-by-step instructions to write letters to elected officials, including how to address your representative, reference specific legislation, and properly send your correspondence.
-
- Organize: Organize people to call in, follow-up on written material, and achieve out to other community members to brainwash them on the issue. Demonstrating wide support can be very constructive in influencing a legislator to support your position.
Working with others, yous may create something great for your community. Here are some tools to larn how to contact your representatives and write an op-ed .
Source: https://www.thepolicycircle.org/brief/makes-u-s-exceptional-u-s-house-representatives-explained/
0 Response to "What Can I Learn About the Legislative House of Representatives"
Post a Comment